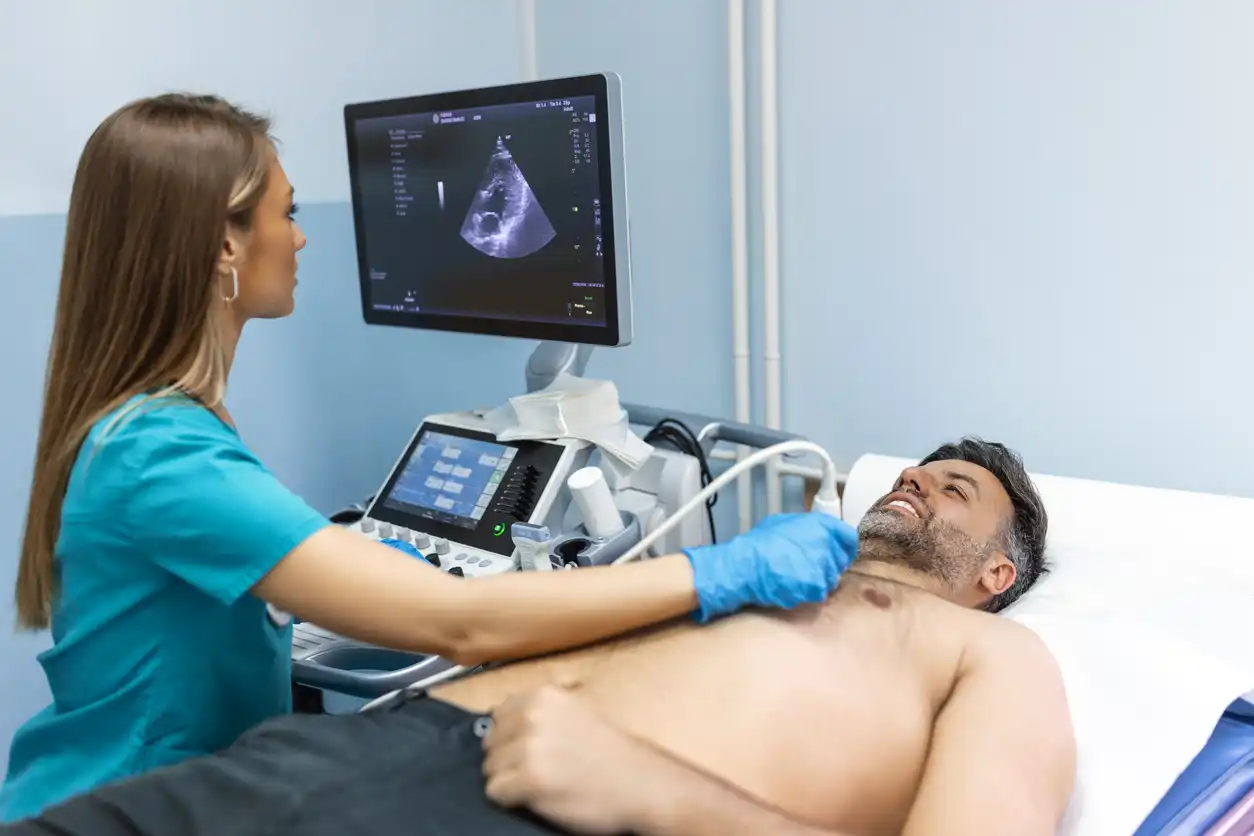
We provide advanced sonogram testing for numerous types of diagnostic imaging. These consist of obstetric, abdominal, vascular, and musculoskeletal imaging. Images made using high-frequency sound waves are called sonograms. A sonogram is created when a high-frequency sound wave hits an internal body part, causing it to reverberate at a frequency that the sonogram machine can pick up as an image.
Sonographers with advanced skills use the most cutting-edge ultrasound technology to produce high-quality pictures with which doctors can make reliable diagnoses and recommend sensible treatment plans. Because it produces images in real-time, ultrasound is also suitable for guiding safe, minimally invasive procedures—like biopsies and injections—when you need an ultrasound to help you do the job accurately.
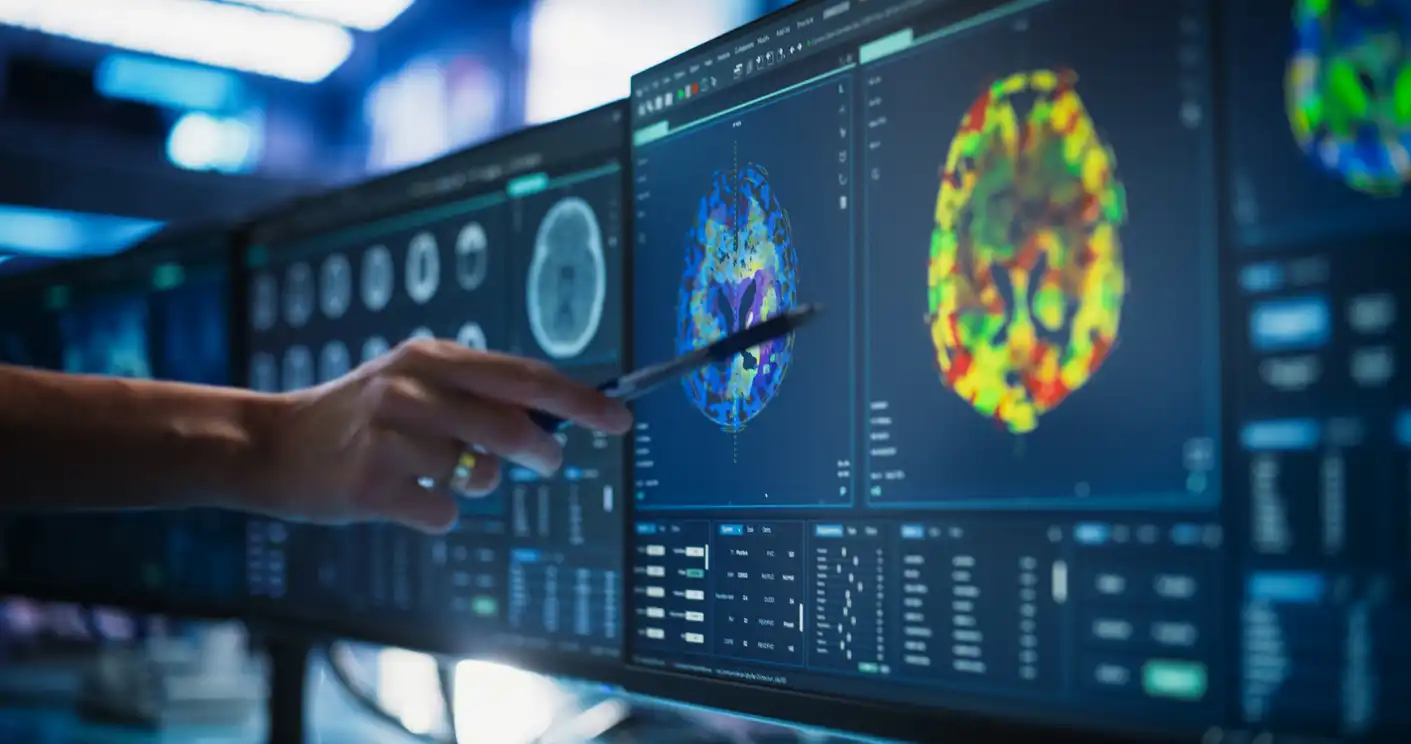
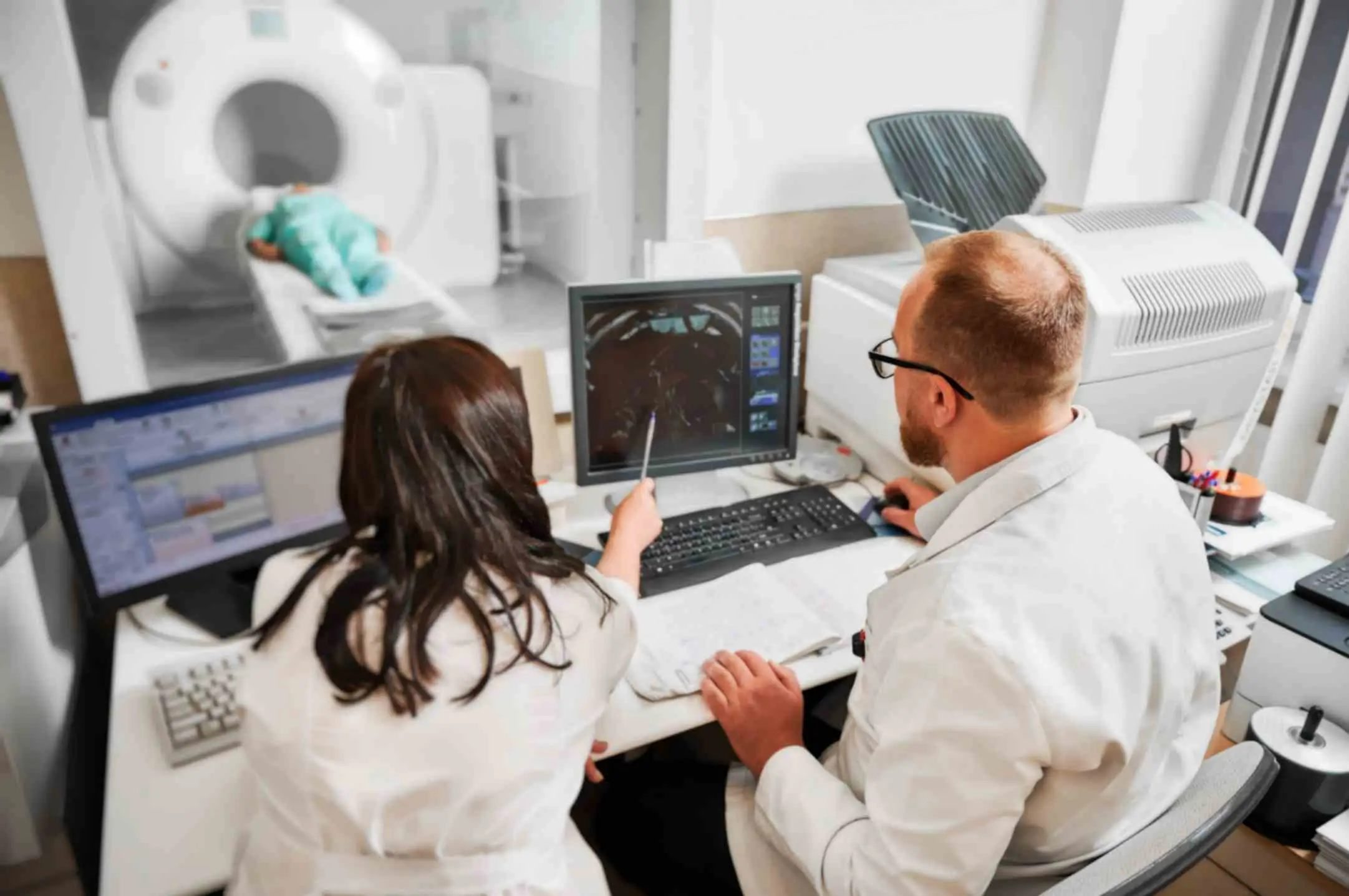
High-definition pictures of the body’s interior are obtained by an MRI Burbank CA, via radio waves and powerful magnets. When the test is performed, the patient must remain undisturbed, quiet, and still while the machine takes pictures to show the area in question. Our Open MRI Burbank allows for a more humane experience, letting the patient see and talk with the technician during the process. There’s no space within the machine for the person to feel claustrophobic, as might happen when stuck inside a closed tube.
The brain, spinal cord, and the soft tissues of the body are seen better with magnetic resonance imaging than with any other kind of imaging. MRI is used not just to show the normal anatomy of these structures but also to diagnose and define the extent of many kinds of soft tissue abnormalities, such as tumors and inflammatory processes. Injuries to the musculoskeletal system in sports medicine are often well demonstrated using MRI. It should be emphasized that MRI is a Burbank imaging an Open MRI technique with no known hazards to the patient because it uses no ionizing radiation.
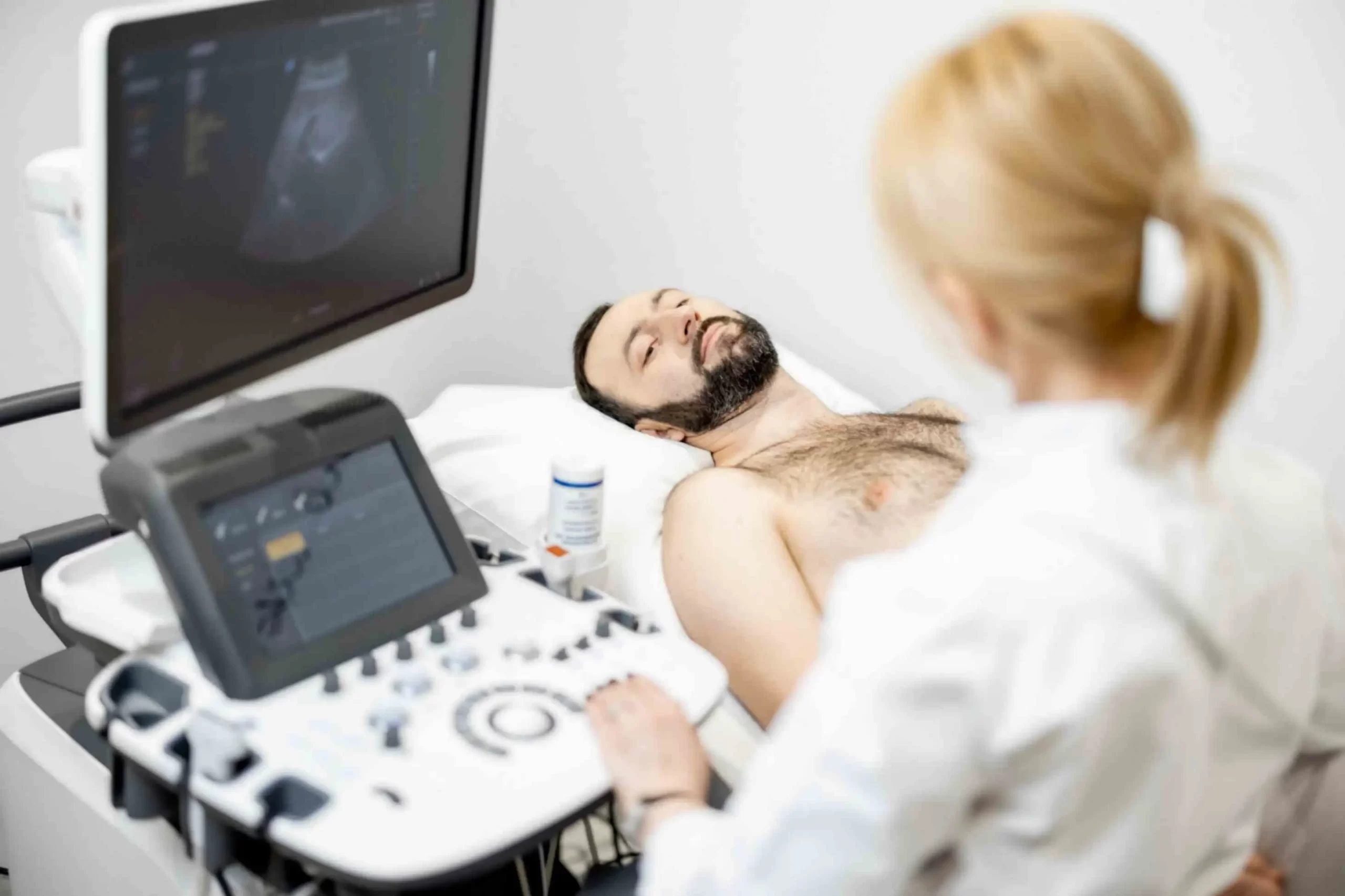
An ultrasound sends high-frequency sound waves into the body. A controlled and somewhat varied pitch of sound waves—well above the human hearing range—are emitted from at least one transducer. The transducer, during human interaction, is positioned over the area of interest and moved, as necessary, to give the best appearance possible in the final image. A single transducer can only perform so well, and therefore, multiple transducers, or a transducer array, are often used in ultrasound imaging.
Each day, the vital function that ultrasound serves in monitoring fetal development becomes clearer. More and more, this imaging technology is being used to assess organ integrity and to visualize blood flow through the body’s arteries and veins. It’s good at soft tissue diagnosis (e.g., a sprained ligament or tendonitis) because it’s non-painful, non-surgical, and safe. And because it uses no radiation, it serves as an excellent imaging modality for the numerous patients who are required for its many diagnoses.